Creating digital musical resources for young people with special educational needs
We listen to music with our ears but I like to think that we perceive music with all of our other senses, intellect and emotions.
For several years now, I have been using multi-sensory methods to teach music to young children. Originally conceived as a way to help children gain confidence with music notation, my ‘Rhythm Circle approach’ rapidly developed from just using a few musical games and activities into my personal music education approach.
It is magical to engage ALL the senses (touch, movement, hearing, sight, smells and tastes) in the learning of music.
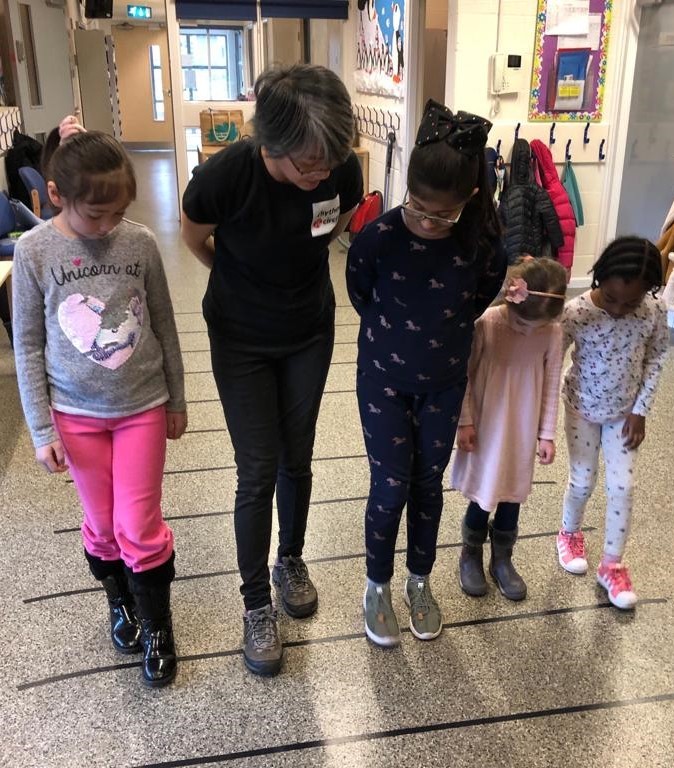

Musical multi-sensory learning: stepping on lines and spaces on a floor stave 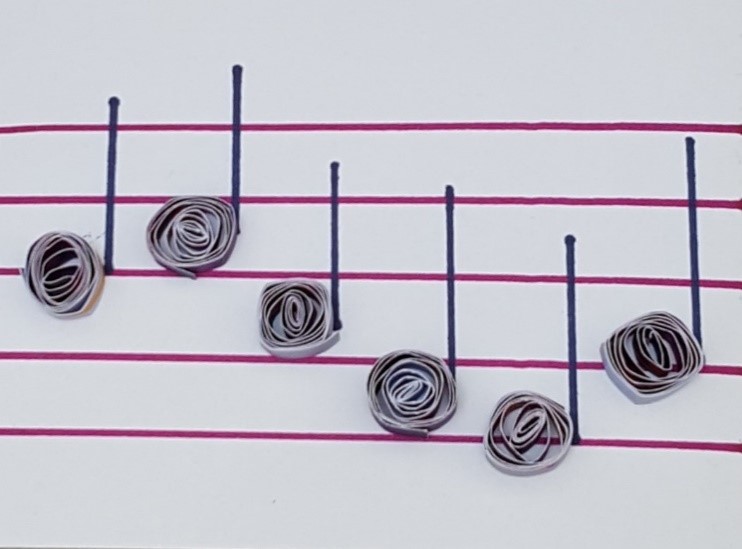
Quilled note heads placed in spaces and lines on a musical stave
Take for example the concept of musical tempo – a child might listen to examples of fast and slow music and be taught the words allegro and lento for fast and slow. How much more profound that learning would be if they could also respond to tempo by:
– movement (moving to the speed of the music)
– choosing visual shapes (NO ONE ever chooses to paint blobs on the side of a Nissan Micra to promote speed but an aspiring speedster might opt for some go-faster stripes)
– by using scents which support a particular level of activity (the aroma of zingy lemons is said to energise whilst lavender calms).
Because multi-sensory learning activates and strengthens connections between different areas of the brain, learning is more deeply embedded in the mind of a learner. Hence its wide-spread use amongst educators working with children with special educational needs.
The term ‘neurodiversity’ is increasingly used instead of ‘special educational needs’ as it focuses on the positive qualities of thinking and learning differently. It encourages us to consider people who have neurological differences as ‘different’ not ‘disabled’.
Earlier on in May 2020, I heard from colleagues interested in good quality digital resources which could support artistic work in schools and communities. The pandemic has wiped out most of the support which special needs communities relied on (in-school sessions with teachers and visiting specialists, community support groups). What could we do to help?
The whole world had gone online in a mad rush to survive and music was no exception. Everything has to be digitized including delivery of my Rhythm Circle sessions. But how? Was it still possible to use multi-sensory approaches…digitally?
Feedback from busy families indicated that printed-off worksheets were not always welcome or helpful. Guided live sessions were more appropriate. There had to be some way of making all these resources link up in a more sophisticated way.

I happen to be married to a software programmer. As our lockdown family project, my long-suffering husband had been persuaded to try his hand at turning some Rhythm Circle games into online games. Maybe we could go further and create some online musical games and activities to help neurodiverse children learn music?
But digital games are expensive to produce. The Arts Council of England Project Grants programme had just re-opened so I hurriedly put together an application. Cue much excited screaming when my project was actually accepted!
Presently, my team and I are three weeks into the Rhythm Circle Digital Games Project. We hope to complete all of our musical games before Christmas 2020: Musical Sudoku, ‘Run Faster’ (a Jack and the Beanstalk – inspired game teaching musical tempo), and ……a yet-to-be-decided graphic score activity.
All this will be trialled in January 2021 by target groups representing primary-aged children, pre-schoolers and neurodiverse young people.
We have almost completed the initial consultation stage, taking on board advice from consultants (special educational needs, Early Years and digital specialists) and feedback from neurodiverse communities.
Burning question: how DO you actually go about making a resource suitable for neurodiverse people? Which type of neurodiversity should we address? Consultant play therapist Andrew Kay provided a starting point with his advice “It is very likely that someone who has one type of learning difference also has another. For example, an autistic person can also be dyslexic.”
Co-occurence of Specific Learning Difficulties
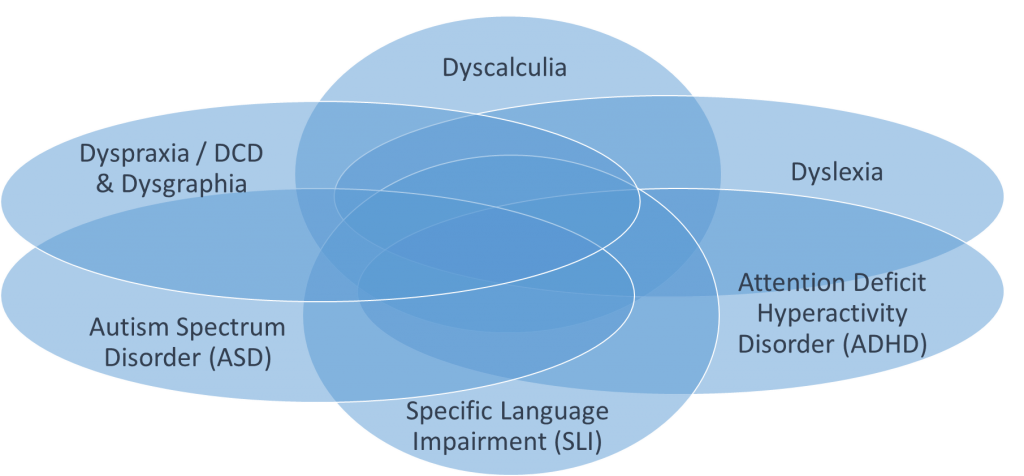
(source: British Dyslexia Association)
So, we started to research characteristics common to many neurodiverse people e.g. poor working memory, problems with sensory processing.
Online games are primarily visual so we need to ensure our games would be visually supportive for people who have problems with reading (dyslexia) or who use eye gaze technology (users are those who have limited mobility or who are locked-in due to a variety of conditions ranging from cerebral palsy and strokes to muscular dystrophy). The British Dyslexia Association has a ‘Dyslexia friendly style guide’ which lists useful adaptations which one can use for written texts.
Digital consultant Wayne Smyth (Trifort Solutions) suggested creating a ‘filter’. This would enable the user to experience the games via a specific route tailored to their learning age and needs, and create a more personalised experience.
Presentation of information in the games and the accompanying explainer videos would need to be paced to allow for more ‘thinking time’. The videos themselves would be better done in the form of high-contrast simple cartoons instead of live-capture – as one school told us ‘The children are tired of looking at people all the time!’.
I am very lucky to be supported by the wonderful Attenborough Arts Centre on this project. They are supporting Rhythm Circle’s inclusive work by facilitating conversations with teachers and families of young people with special educational needs and disabilities. “We’re really interested in how the artists involved are developing resources and workshops and are always keen to promote artist development as part of a collaborative process with young people. The project findings will feed into our wider work as part of our 4-year SENsory Atelier programme, and as ever we’re delighted to support a project that encourages sharing of best practice amongst a wide team of expert artists and educators.”
In Part 2 of this blog, I would like to share an account of how we borrowed from best practices in Early Years teaching approaches.
Find out more about the Rhythm Circle Digital Games Project and its trials here
